The Pervasive Learning Model
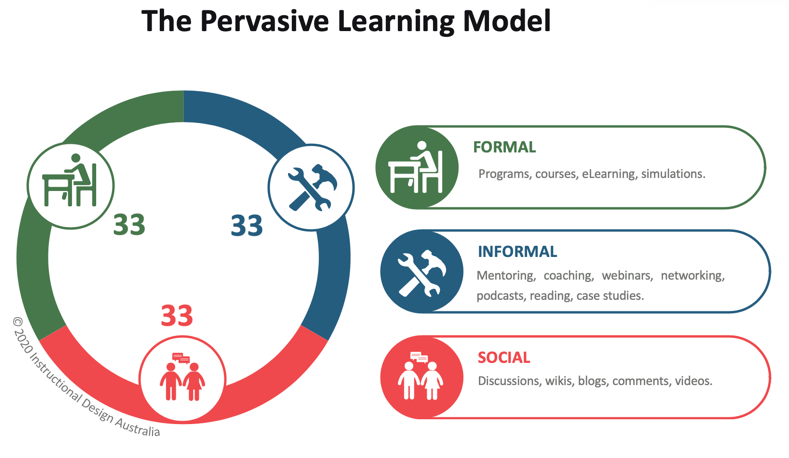
Pervasive learning, also known as P-Learning or the 3-33 Model, was developed by Dan Pontefract in 2013. He described it as “learning at the speed of need through formal, informal and social learning modalities” [1].
Like the 70:20:10 Model, pervasive learning sees learning as continuous and occurring beyond any formal learning ‘event’. The Pervasive Learning Model, however, posits that 33% of learning evenly occurs via formal, informal and social opportunities.
Pervasive learning acknowledges that there are learning opportunities everywhere in everyday life, not solely in structured programs. It recognises that employees gain critical learning insights through conferences, mentoring, podcasts, videos, blogs, wikis and discussions [2].
Given this, the valuable capabilities of digital learning technologies and tools become obvious. They make learning accessible at any time, from anywhere [3].
In what other ways are eLearning tools and technologies key to pervasive learning?
They’re Empowering: Just-in-time information
Teams and individuals can take initiative to solve their own problems by sourcing relevant information from a wealth of accessible resources by using digital tools. This includes workplace documents, online articles, videos, websites and podcasts – all available at their fingertips.
They’re Convenient: Learning at your own pace
Pervasive learning allows learners to expand their knowledge base and improve their skills when it is convenient for them – even when working remotely – making it an ideal model for autonomy-driven adult learners [4].
They’re Social: Collaborative environment
Wikis, forums, blogs and other social eLearning tools provide opportunities for learners to engage in shared learning by supporting one another, seeking feedback, working together to solve problems and exchange information, learning and experiences with peers.
eLearning technologies and tools provide a means of implementing the Pervasive Learning Model through accessible, convenient and effective delivery methods that are flexible in time and place.
To learn more about developing eLearning programs, read:
Related Articles and Blogs
- The 70:20:10 Learning Model
- The AEE Learning Model
- How-To: Design For Online Courses
- Embedding Activities in Learning Design: Why Leaders Matter
- Merrill’s Instructional Design Principles
Read more of our blog articles here.
References
[1] Pontefract, D. (2013) Flat Army: creating a connected and engaged organization. Wiley.
[2] WIOA Australia (2019). The Technical Competency Handbook: Knowledge, skills and competency development for water industry operations staff.
[3] Koondhar, Yaqoob & Malook, Muhammad & Chandio, Fida & Shah, Asadullah. (2015). Pervasive learning environment with emerging technologies and learning transformation.
[4] Pink, D. H. (2009). Drive: The surprising truth about what motivates us. New York, NY: Riverhead Books.