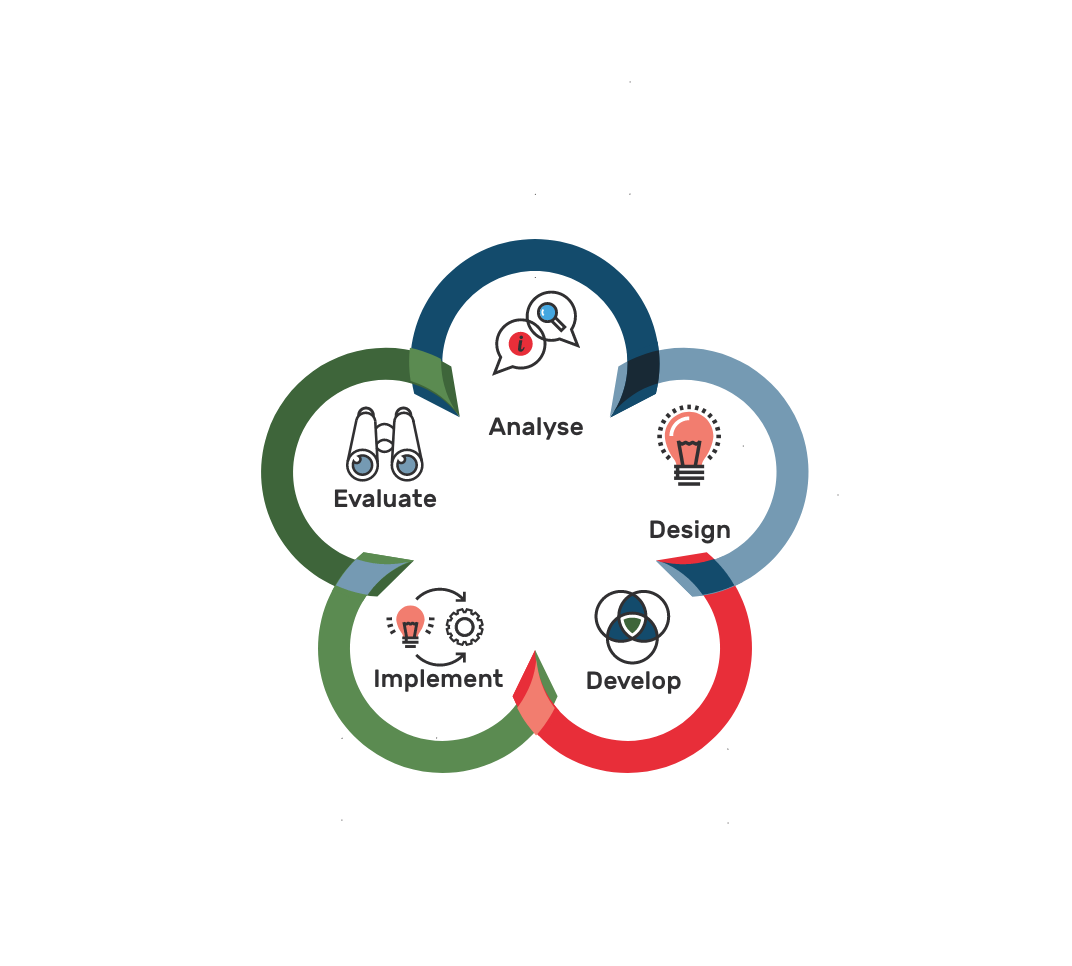
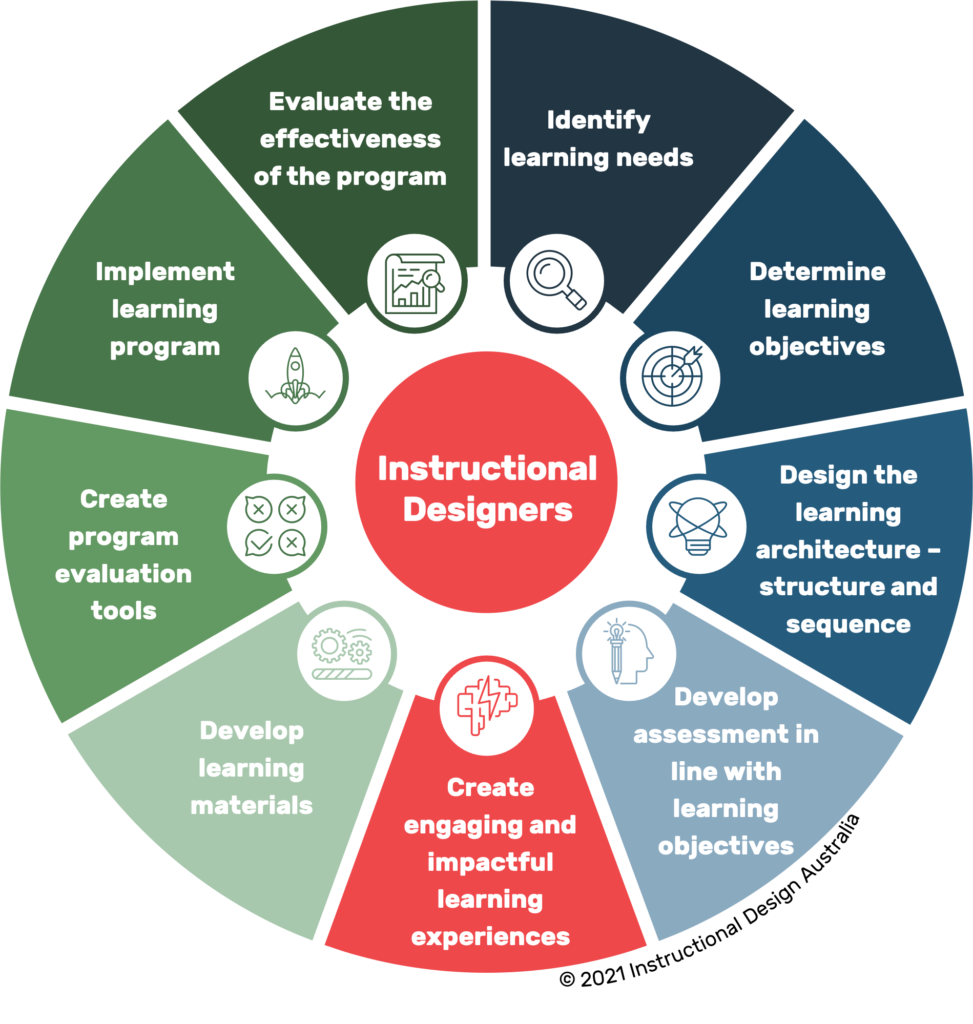
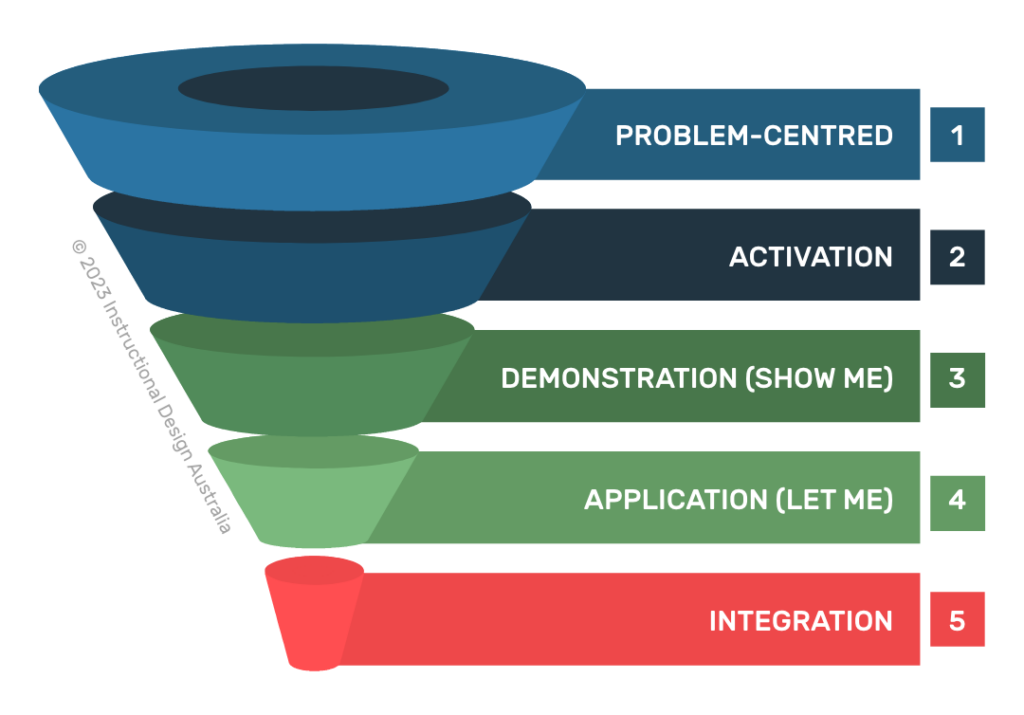
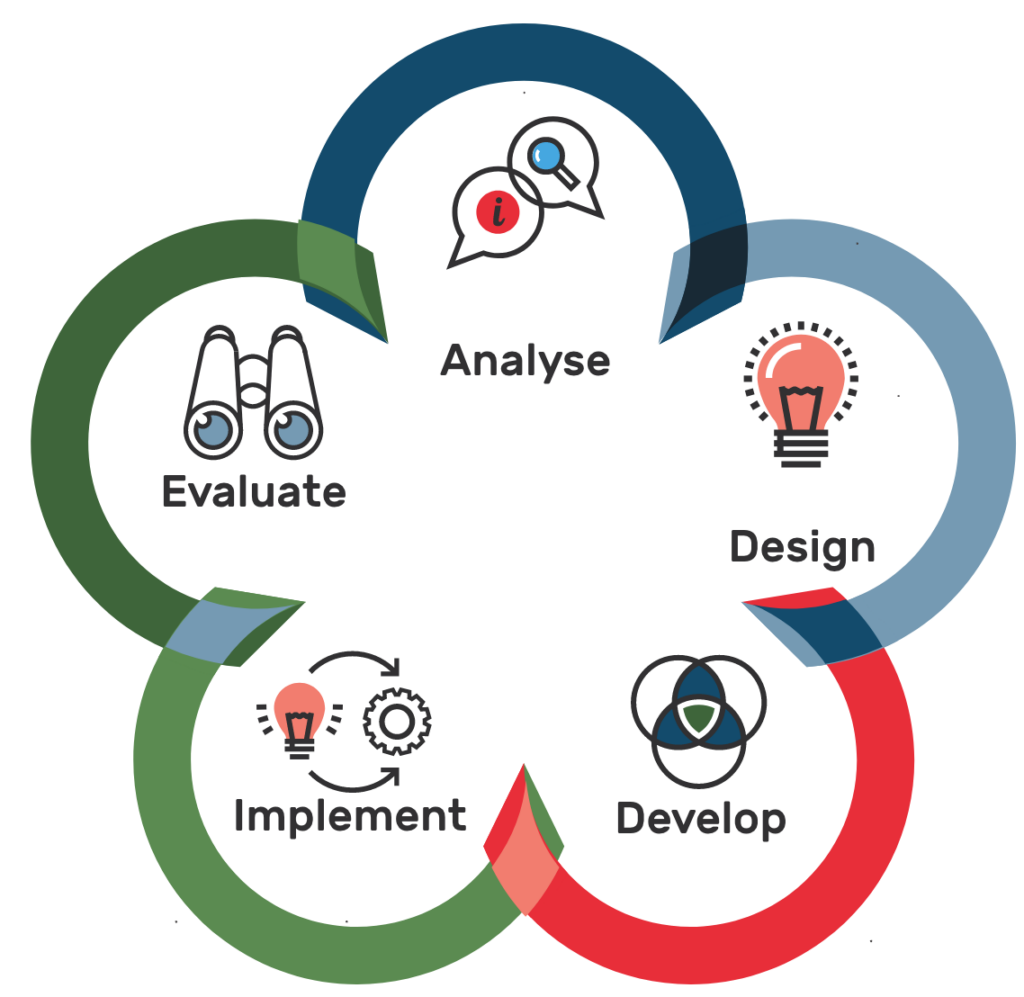
Although many organisations use these terms interchangeably, each role serves a distinct purpose in the educational development landscape. Let’s explore how these roles differ (including scope, requirements and focus) and where they intersect.
Educational Designer: The Strategic Architect
Educational Designers sit at the strategic level of learning development. They require formal qualifications in Learning Sciences and current pedagogical/adragogical knowledge. Think of them as the architects of learning – they:
- Design broad educational frameworks
- Work across multiple disciplines
- Drive pedagogical/adragogical innovation
- Evaluate educational effectiveness
- Shape institutional learning strategies
Learning Designer: The Subject Specialist
Learning Designers focus on specific subject areas or courses. They bridge the gap between educational strategy and practical implementation. Their role typically involves:
- Developing detailed course content
- Working closely with subject matter experts
- Creating engaging learning experiences
- Ensuring content alignment with learning objectives
- Maintaining pedagogical consistency
Instructional Designer: The Technical Implementer
Instructional Designers excel in creating specific learning materials and experiences. They transform educational strategies into tangible learning assets. Their focus includes:
- Developing eLearning modules
- Creating interactive content
- Implementing learning technologies
- Designing assessment materials
- Building practical learning activities
The Changing Face of Learning Design in 2024: Industry Insights and Trends
The Big Picture: Learning Design is Booming
Let’s start with some eye-opening numbers: 86% of organisations now see reskilling as make-or-break for their future success (Deloitte, 2024). And they’re putting their money where their mouth is – nearly half of L&D departments (39%) are working with bigger budgets than last year (LinkedIn, 2024). 45% of organisations expect team size to increase (LinkedIn, 2024).
Show Me the Money: Current Salary Landscape
Curious about earning potential? Salary ranges are looking healthy across the board (Seek.com.au, April 2024), with significant growth over the past year:
- Educational Designers:
- Average range: AUD $90,000 – $120,000
- Top advertised salary: Up to $135,000
- Instructional Designers:
- Average range: AUD $85,000 – $110,000
- Top advertised salary: Up to $130,000
- Learning Designers:
- Average range: AUD $80,000 – $105,000
- Top advertised salary: Up to $125,000
Location Impact on Salaries
According to Seek’s Salary Spotlight (April 2024) and their Regional Insights Report (Q1 2024), location significantly influences earning potential:
- Major Cities Command Premium Rates:
-
- Sydney leads at 8.3% above national median
- Melbourne follows at 7.1% above national median
- Remote Work:
- 34% of learning design roles offer remote options
- Hybrid roles make up 25% of positions
- Fully remote: 15% of listings
The Changing Nature of Learning Design
Here’s something interesting: 83% of L&D roles say their role has become more cross-functional (LinkedIn, 2024). Think of it as breaking down silos – learning design is no longer just about creating courses; it’s about shaping entire learning experiences.
58% of organisations now offer hybrid learning options, with 71% prioritising digital learning solutions (LinkedIn, 2024).
What’s Driving These Changes?
Organisations are getting serious about learning – really serious. research shows:
- 89% rate capability building as a top priority (Deloitte’s 2024)
- 47% are actively redesigning jobs to integrate technology (Deloitte’s 2024)
- 39% have more budget than the previous year (LinkedIn, 2024)
- 86% identify reskilling as important for future success (Deloitte, 2024)
The Bottom Line
The numbers tell a clear story: learning design is evolving from a support function to a strategic driver of organisational success. Whether you’re in the field or considering it, the opportunities for impact (and growth) have never been better.
Become an Instructional Designer
Join a profession that combines creativity, technology, and human-centered design. Our hands-on course turns theory into practice, giving you the tools, templates, and techniques to design effective learning solutions. Created by industry-leading instructional designers who’ll coach you personally, you’ll work on real projects, get expert feedback, and build your portfolio while you learn.
What Sets Our Course Apart:
✓ 12-week hybrid learning experience
✓ 3 one-on-one coaching sessions with industry experts
✓ Comprehensive ID toolkit with lifetime access
✓ Portfolio-building projects
Looking for a Job as an Instructional Designer or Learning Designer in Melbourne, Sydney, Brisbane or Perth?
We are always looking for talented instructional designers to join our team in Melbourne, Sydney, Perth and Brisbane on an independent contractor or casual employee basis to provide instructional design support on specific projects. Our projects typically vary in length from 1 to 12 weeks, so we may be able to offer flexible engagements around your other commitments and availability (including work from home, flexible days and hours). Learn More
References:
- Deloitte. (2024). Human Capital Trends 2024. Retrieved from deloitte.com/insights/capital-trends
- LinkedIn. (2024). Workplace Learning Report 2024. Retrieved from linkedin.com/learning/reports
- Seek.com.au. (2024, April). Employment Market Analysis. seek.com.au/market-analysis
- Seek.com.au. (2024, April). Salary Guide. Retrieved from seek.com.au/salary-data
- Seek.com.au. (2024). Employment Report Q1. Retrieved from seek.com.au/market-analysis